Die casting is a vital manufacturing process in modern industry. It efficiently shapes complex metal components with excellent precision and surface quality. Choosing the right die casting method impacts production speed, product quality, and cost-effectiveness. By comparing the unique features of hot and cold chamber die casting, you can better match the right method to specific metal components. This article explores the differences between these two methods to help you make informed decisions based on your needs.
What is Hot Chamber Die Casting?
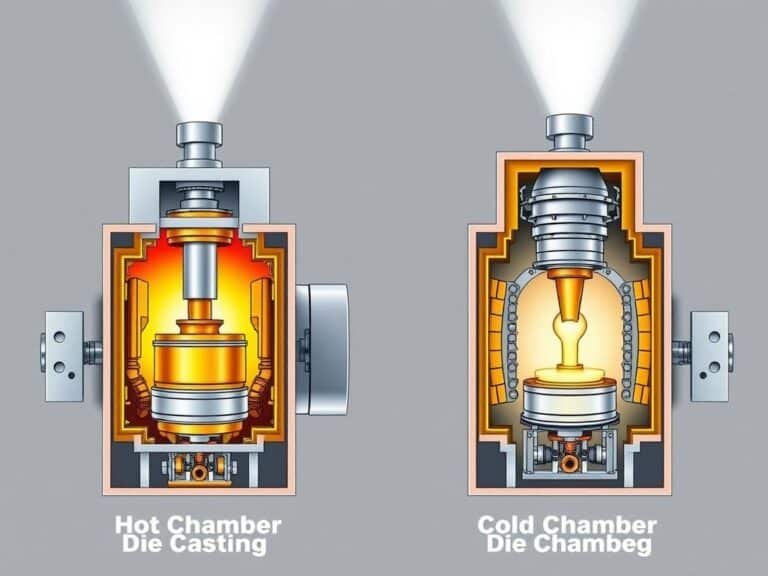
Hot chamber die casting injects molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. Its standout feature is the integration of the melting furnace and injection system. This setup makes processing low-melting-point metals more efficient by eliminating unnecessary transfer steps, which boosts production speed.
The process relies on a gooseneck structure that connects the melting container to the injection device. A hydraulic piston injects molten metal into the mold under high pressure, ensuring smooth and efficient operation. This system can achieve up to 15 production cycles per minute, making it ideal for high-volume production. The method also minimizes metal flow disturbances and reduces the risk of gas entrapment, resulting in high-quality castings with low porosity.
Hot chamber die casting works best with low-melting-point metals that don’t corrode equipment, such as zinc, tin, lead, and some magnesium alloys. These materials ensure long-term equipment stability while keeping costs low. This method produces high-quality, geometrically complex components that are also cost-effective.
Advantages:
- Fast production cycles (up to 15 cycles per minute).
- Energy-efficient, reducing overall energy use.
- Produces high-quality castings with low porosity.
- Long mold life and low maintenance costs.
Limitations:
- Only suitable for low-melting-point metals (e.g., zinc, tin, magnesium).
- Not ideal for products requiring very high pressure.
What is Cold Chamber Die Casting?
The key difference in cold chamber die casting is the separation of the melting and injection systems. The metal is melted in an independent furnace and then transferred to the machine for forming. This design is ideal for high-melting-point metals, such as aluminum, magnesium, and copper, as it prevents damage to the injection system from direct exposure to high temperatures.
In this process, molten metal is ladled or poured into the injection chamber. A hydraulic plunger then applies high pressure to push the metal into the mold cavity. This setup allows for better temperature control, reducing impurities and improving casting quality. Cold chamber die casting typically uses higher injection pressures, which enhances the mechanical properties of the castings and reduces porosity.
This method is specifically designed for high-melting-point alloys like aluminum, copper, and certain magnesium alloys. These materials require higher heating temperatures but offer superior strength, corrosion resistance, and conductivity. With advanced cold chamber equipment, manufacturers can produce castings that meet strict industrial standards.
Advantages:
- Handles high-melting-point metals (e.g., aluminum, copper, magnesium).
- Produces dense castings with excellent mechanical properties.
- Suitable for large parts and structural applications.
Limitations:
- Longer production cycles compared to hot chamber die casting.
- Metal transfer steps may lead to oxidation or contamination.
What is the Difference Between Hot and Cold Chamber Die Casting?
Understanding the differences between hot and cold chamber die casting helps manufacturers optimize production strategies. At Yonglihao Machinery, we offer professional die casting services for various metals, including aluminum and zinc, using both methods to address diverse production challenges. Below are the main differences:
Process and Equipment Differences
Hot chamber die casting integrates the melting furnace with the injection system. Molten metal is transferred directly to the mold through a gooseneck structure, simplifying the process. This method is best for low-melting-point metals. In contrast, cold chamber die casting uses an independent furnace. Molten metal is ladled or poured into the shot sleeve, making it suitable for high-melting-point metals.
- Hot chamber die casting: Gooseneck transfer, ideal for low-melting-point metals like zinc.
- Cold chamber die casting: Sleeve plunger system, designed for high-melting-point metals like aluminum and copper.
Production Cycle and Temperature Differences
Hot chamber die casting has shorter production cycles because molten metal is immediately available. It can achieve 400-900 cycles per hour. Cold chamber die casting has longer cycles due to the additional metal transfer steps, typically achieving 50-90 cycles per hour.
- Hot chamber die casting: Maintains a stable liquid state, ensuring consistent quality.
- Cold chamber die casting: Requires cooling during transfer, which lowers efficiency but allows flexibility for high-melting-point metals.
The table below highlights key differences:
| Feature | Hot Chamber Die Casting | Cold Chamber Die Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace/Injection System | Integrated, injection immersed in molten metal | Independent furnace, metal ladled into shot sleeve |
| Metal Casting | Low-melting-point metals (e.g., zinc, lead) | High-melting-point metals (e.g., aluminum, copper) |
| Cycle | Faster production speed | Slower due to additional transfer steps |
| Injection Pressure | Relatively lower | Up to 900-1200 bar |
| Porosity | Low porosity | Higher porosity risk with high-speed injection |
| Best For | Small, high-volume parts | Large, high-strength parts like aluminum die casting |
Applications and Industry Uses
Both hot and cold chamber die casting are widely used in various industries, meeting different production needs.
Hot Chamber Die Casting Applications
Hot chamber die casting is ideal for thin-walled, complex, and high-volume small components. It’s especially useful in industries requiring high precision and efficiency.
- Electronics: Produces small parts like device housings and connectors with high precision and smooth finishes.
- Automotive: Makes lightweight parts like door locks and dashboard frames.
- Consumer Goods: Creates decorative and household hardware that balances aesthetics and cost.
Cold Chamber Die Casting Applications
Cold chamber die casting is better for large components that need high strength and heat resistance. It’s widely used in industries with demanding mechanical and structural requirements.
- Automotive: Produces key parts like engine blocks, radiators, and transmission housings.
- Aerospace: Creates lightweight, high-strength components like structural parts and support frames.
- Electronics: Makes parts with high thermal and electrical conductivity, such as LED heat sinks.
- Industrial Equipment: Produces structural and heat-resistant parts for heavy machinery.
Hot chamber die casting excels in producing small, high-volume precision components. Cold chamber die casting is better for large, high-performance parts. Choosing the right method based on industry needs improves product performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. For high-melting-point metals like aluminum, the cold chamber process is the go-to choice for aluminum die casting.
Conclusion
Choosing between hot and cold chamber die casting depends on your business needs. Whether you need efficient production of small components or high-strength, heat-resistant large parts, the right method will directly impact product performance, cost, and competitiveness.
At Yonglihao Machinery, we offer tailored hot and cold chamber die casting solutions. Our team helps optimize design parameters and select the best process based on your product needs, materials, production scale, and budget. With advanced equipment and strict quality control, we ensure every casting meets or exceeds expectations.
If you’re looking for a reliable die casting partner or have questions about which method to choose, feel free to contact our team anytime.
FAQ
What is the main difference between hot chamber and cold chamber die casting?
Hot chamber integrates the melting furnace with the injection system, ideal for low-melting-point metals. Cold chamber uses an independent furnace, suitable for high-melting-point metals and denser castings.
What metals are commonly used in hot chamber die casting?
Zinc, tin, lead, and some magnesium alloys are commonly used, as they don’t corrode equipment and allow efficient production.
What are the advantages of cold chamber die casting?
It handles high-melting-point metals like aluminum and copper, producing dense, high-strength castings for structural applications.
What are the limitations of hot chamber die casting?
It’s only suitable for low-melting-point metals and cannot handle high-temperature alloys or products requiring very high pressure.
Why is the production cycle of cold chamber die casting longer?
The process involves ladling metal from an independent furnace, adding transfer steps that extend the cycle.
How to choose the appropriate die casting method?
Evaluate based on metal type, product size, batch needs, and budget. Hot chamber is best for small, low-melting-point components, while cold chamber suits large, high-strength parts.
How efficient is hot chamber die casting?
It’s highly efficient, achieving 400-900 cycles per hour, making it ideal for high-volume production.
Is cold chamber die casting suitable for complex shapes?
Yes, it can produce high-strength, complex components through high-pressure injection, though the production cycle is longer.