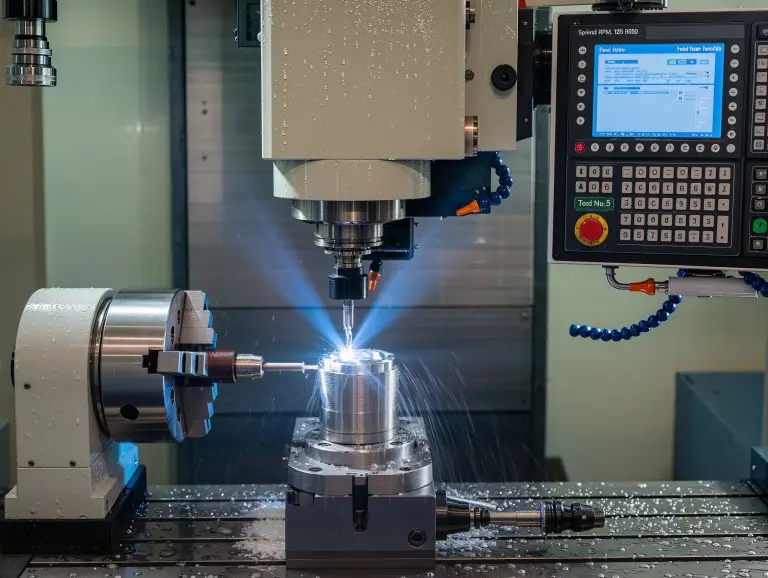
CNC machining is now a key part of modern prototyping, changing how ideas turn into real models. Its precision, speed, and flexibility make it vital for product development. Designers can create better prototypes faster, improving quality and reducing time to market. Prototyping has evolved from slow, detailed handcrafting to advanced CNC technology. This shift has brought greater accuracy, efficiency, and innovation. In this article, we’ll look at the benefits, challenges, and uses of CNC machining. We’ll also share tips to help you get the most out of this powerful tool.
Traditional vs. Rapid CNC Prototyping
Prototyping has come a long way, moving from manual craftsmanship to advanced technology. Traditional methods relied on handcrafting, which offered fine details but was slow, labor-intensive, and hard to replicate with accuracy.
Modern rapid prototyping, like CNC machining, has changed the game. Using software to control machines, CNC machining produces precise and complex parts much faster. This speeds up the process and lowers costs during design revisions.
One major benefit of CNC machining is its consistency. Manual methods often fail to replicate intricate designs accurately. CNC machines, however, ensure every prototype matches the digital design perfectly. They also work with many materials, such as metals, plastics, and wood, giving designers more options for testing and functionality.
CNC machining has made prototyping faster, more accurate, and versatile, meeting the needs of modern design with ease.
Advantages of CNC Machining for Prototyping
CNC machining is widely used in prototyping for its high accuracy and precision. It is also chosen for its cost-effectiveness, efficiency, consistency, and versatility in using materials.
High Accuracy and Precision
CNC machining can create parts to the exact design specifications. This ensures a high degree of accuracy and precision. This is especially important for complex prototypes. Even small deviations can affect the functionality and appearance of the entire prototype. CNC machining can accurately replicate the design documents, ensuring that every detail is as expected.
Cost-effective and efficient
CNC machining offers significant time and cost savings when manufacturing prototypes compared to traditional handcrafting. CNC machining is a highly automated process. This reduces the likelihood of manual errors and rework. It also increases productivity. This means that even complex prototypes can be completed in less time and at a lower cost.
Consistency and repeatability
CNC machining provides superior consistency and repeatability in prototype production. Each prototype or part will maintain consistent quality and accuracy, no matter how many times it is produced. This is especially important for prototypes that require multiple iterations or mass production.
Versatility in Material Use
CNC machining is highly versatile, supporting a wide range of materials like metals and plastics. This flexibility lets designers pick the best material for their prototypes, whether they need strength, durability, or cost savings. Its ability to handle diverse materials makes CNC machining a valuable tool for many uses.
With its precision, efficiency, consistency, and repeatability, CNC machining is the top choice for modern designers and engineers. It keeps up with the fast pace of innovation and prototyping, offering a reliable and efficient way to bring ideas to life.
Limitations and Challenges of CNC Prototyping
CNC prototyping offers significant advantages in many areas, but it also faces limitations and challenges. These include high knowledge requirements, potential material waste, design geometry limitations, and cost challenges. You should take these into account when choosing the right manufacturing method.
Requires technical expertise
CNC machining requires specialized technical knowledge and experience. Operating a CNC machine is not a simple process; it requires an in-depth understanding of the machine, materials, and software. Designers and engineers must have the expertise to utilize this technology effectively. This may limit its use to beginners or small businesses.
Material waste considerations
CNC machining is a material reduction process. It can generate more material waste than additive manufacturing, such as 3D printing. When cutting and carving out parts from a block, the leftover material is often not reused. This can increase the total cost of the prototype and have an impact on the environment.
Geometric Constraints in Design
CNC machining can be limited when dealing with certain complex geometries. Advanced CNC machines, such as 5-axis machines, can handle complex designs. However, certain internal structures and subtle features may be difficult to realize with CNC machining. This is especially true when deep holes or very fine details are involved.
Cost comparison with 3D printing
CNC machining is typically more expensive than 3D printing. This is especially true for single-piece or low-volume prototypes. CNC machining may be more cost-effective for high-volume production. However, 3D printing may be a more economical option for initial prototyping. It requires rapid iteration and modification.
Further Reading: CNC Machining vs. SLS 3D Printing
CNC Prototyping in Various Industries
CNC prototypes are important in several industries, like aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer products. They are highly accurate, reliable, and work with multiple materials.
Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, precision and strength are essential in making parts. CNC machining is used to manufacture key components for spacecraft, like engine parts and structural assemblies. For example, aluminum alloys are widely used to make aircraft wings and fuselage structures due to their lightness and strength. the high precision of CNC technology ensures that these parts can withstand extreme environments and stresses.
Automotive
The automotive industry uses CNC machining to create engine components, drivelines, and body parts. For example, it produces high-performance pistons and crankshafts that need extreme precision and wear resistance. CNC machining is also essential in automotive prototyping. It quickly makes prototypes of new models, allowing for fast testing and evaluation during the design phase.
Medical
In the medical industry, CNC machining is used to manufacture surgical tools. It is also used to make orthodontic devices and implants. For example, titanium and stainless steel are often used in the manufacture of human implants such as joint replacements and dental implants. This is because these materials are biocompatible and resistant to corrosion.The advantages of CNC machining in medical devices include high precision, consistent quality, and the ability to work with specialized materials. These strengths make it a key technology for producing safe and reliable medical equipment.
Consumer Goods
In the consumer goods sector, CNC machining is used to manufacture a variety of precision components. These include housings for electronic devices, customized jewelry, and high-end audio equipment. These applications often require a high level of customization and aesthetics. CNC machining provides the flexibility and precision to achieve these requirements.
CNC Prototyping Considerations and Tips
Manufacturers use CNC prototyping to ensure that parts are accurate and meet standards before high-volume production. Want to make a CNC prototype of your design? Here are some suggestions.
Reduce Prototype Complexity
Complex designs may sound good, but they usually aren’t. One thing to keep in mind with CNC prototyping is that complex parts cost more. In addition to the cost, it takes a long time to set up a machine for a design with many angles and undercuts. This usually makes development time longer. As a result, complex designs can make the process of making a product more expensive and take longer to complete.
Using Default Tolerances
In most cases, using default tolerances is the best approach. To get better tolerances, you may need special cutting tools and additional fixtures, which will increase production costs. In most cases, let the skilled engineer working on your project select the best tolerance grade for your product sample.
Consider the Geometry of the Tools to Be Used in the Design
The axial characteristics of the tool or the object to be machined should be taken into account when performing prototype CNC machining. This is because the machining process takes place by rotation. Most cutting tools are round and can only cut a certain length. This means that the shape of the tool affects all cutting processes.
Choose an Experienced CNC Prototype Manufacturer
More importantly, you should work with an experienced CNC manufacturing expert. This is because they can focus on streamlining the process to produce good prototypes. The expert will also consider the geometric limitations of the cutting process in order to produce the desired prototype design. Without a skilled prototype maker, it will be difficult to maximize the use of CNC machining technology in prototype development.
Conclusion
CNC machining is key to modern rapid prototyping. It offers precision, efficiency, and material versatility. This technology helps designers and engineers turn ideas into physical models fast. It speeds up product development. CNC machining handles complex shapes, strong components, or delicate custom parts with ease. It delivers reliable, high-quality results every time. As a trusted rapid prototyping provider, yonglihao uses CNC machining to meet diverse needs with accuracy and consistency.
FQA
How long does it take to produce a CNC machining prototype?
Yonglihao Machinery’s production time depends on the complexity of the prototype and the materials used and generally ranges from a few hours to a few days.
How much does a CNC machining prototype cost?
The cost varies depending on the size of the prototype, the materials used, and the complexity of the design. Usually, it needs to be estimated on a project-by-project basis.
What materials can be used for CNC machining prototypes?
Yonglihao Machinery supplies a wide range of materials to choose from, including a variety of metals (e.g. aluminum, stainless steel), plastics (e.g. ABS, polycarbonate), and more.
What is the difference between CNC machining and 3D printing prototyping?
CNC machining is subtractive manufacturing for harder materials, while 3D printing is additive manufacturing for complex geometries.
How accurate is CNC machining prototyping?
CNC machining offers extremely high accuracy for applications that require precise dimensions and smooth surfaces.