In manufacturing programs, laser cutting and plasma cutting are both processes that use heat to cut metal. How to choose is then a job that needs to be analyzed. Each of these two thermal cutting methods has its own type of work for which it is suitable. Which method is best for you depends on your budget, and the type of material to be cut. In addition, your requirements for cutting accuracy and the speed at which you wish to complete the job will also influence your choice.
We will discuss the pros and cons of plasma cutting and laser cutting in this article. By comparing them, you will be able to make the right choice for you.
Table of Contents
What Is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is a method of cutting a sheet of material without touching it. A focused laser beam precisely melts and vaporizes the material to cut out complex shapes. And in 1964, an industrial company first used a laser cutter to make molds.
Over time, laser-cutting tools have gotten better and better. Yonglihao Machinery can provide customers with high-quality laser cutting services. With tolerances as low as ±0.003 mm, CNC laser cutters can precisely control the movement of the laser head through G and M codes.
How Does Laser Cutting Work?
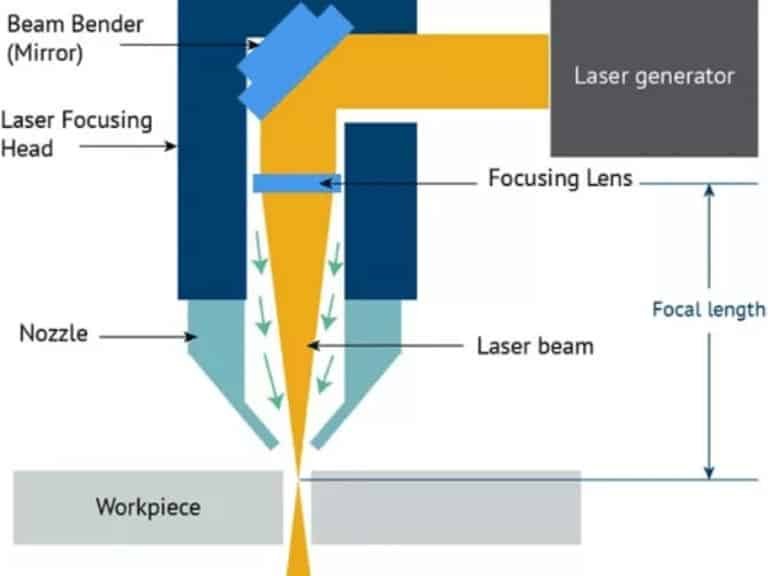
The laser cutting process is accomplished by a complex laser system that contains many components. The functions of these components include manufacturing the laser and guiding the beam along a set cutting path.
The first step in the process is to create the laser. An electric light source (spark) accelerates the atoms on the laser medium (e.g., carbon dioxide or fiber optics). As a result of this effect, a very concentrated beam of light is produced, which is then intensified by mirrors and sent to the cutting area. A set of focusing lenses then converges the light into a bright spot. As it passes through the nozzle, the energy density increases.
In addition, a laser cutting torch or focusing head allows the nozzle head to move along a set path controlled by a CNC program. As the focused laser heats a small area, it melts the material. And a stream of gas blows the melted material away.
Types of Laser Cutting Machines
There are three main types of laser cutting machines used in production. They are named after the medium used to create the laser beam: CO₂, fiber optics, and Nd:YAG crystals. These laser media have different wavelengths, 10.6 µm, 1.06 µm, and 1.06 µm respectively. Variations in wavelength affect the effect of the laser on different materials. For example, some materials absorb specific wavelengths better than others.
- CO₂ Laser Cutter: It uses a carbon dioxide gas mixture to produce a focused laser beam. It is best suited for cutting non-metallic sheets such as plastic and wood.
- Fiber Laser Cutting Machine: Light is amplified through an optical fiber to produce a laser. It is best suited for cutting metal sheets.
- Nd: YAG: The laser medium of this type of laser is made of neodymium-doped YAG crystals.
What Is Plasma Cutting?
The process of cutting sheet metal in a stream of hot ionized gas is known as plasma cutting. An electric spark causes a large amount of heat to be generated in a compressed gas (such as air, hydrogen, or argon), causing the atoms to want to move. The molecules then keep hitting each other, separating them from the gas. This is known as plasma, and the process can reach temperatures in excess of 20,000°C.
In industrial equipment, CNC plasma cutting machines cut materials precisely by controlling the plasma flow. A plasma cutter can cut much thicker metals compared to a laser cutter. It can even cut metals up to 1.5 inches thick.
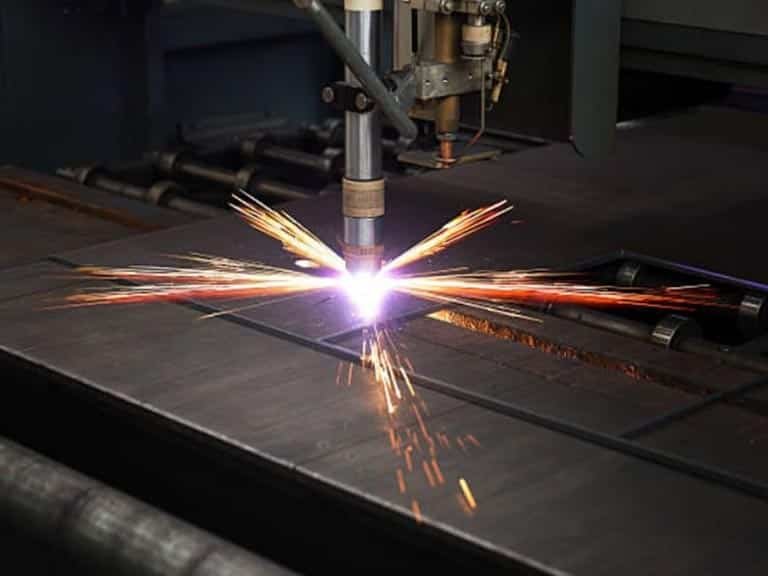

How Plasma Cutting Works?
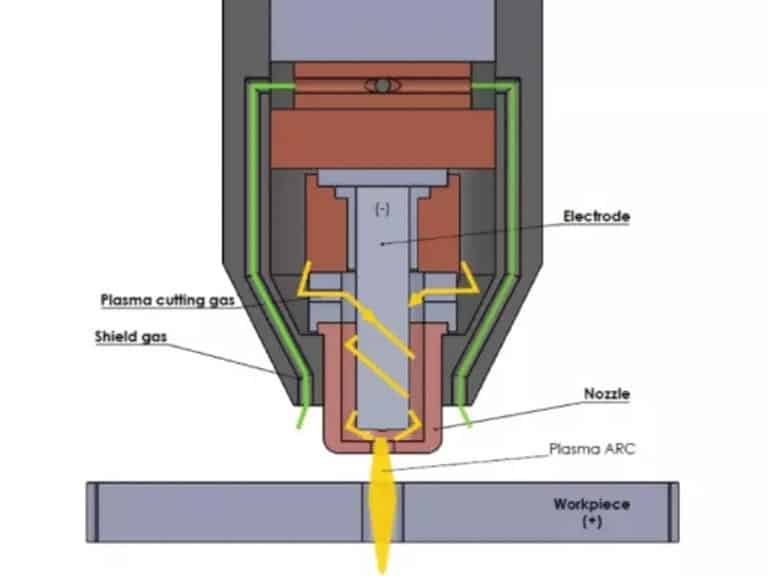
The plasma torch is the most important piece of equipment for this process. It consists of several parts, including an electrode, a gas source, a nozzle, and a protective gas. The electrode creates an electric arc in a compressed gas, such as air or an inert gas. The nozzle then directs the plasma jet onto the target.
When the plasma jet strikes the work surface, it heats the area and melts the material. At the same time, the high-velocity jet sweeps away liquid material from the cut.
Types of Plasma Cutting Machines
Plasma cutting machines can be equipped with different types of cutting heads for cutting materials on the table. Common types include air, oxygen, HD, and CNC plasma cutters.
- Air Plasma Cutter: This type of cutter uses air as the laser medium. It is best suited for cutting small parts or small quantities of parts.
- Oxygen Plasma Cutter: The plasma formed when the oxygen molecules are ionized is more precise and complex than air cutting.
- CNC Plasma Cutting Machine: The cutting path can be controlled by a computer, which ensures that the cut is precise and consistent. Most businesses use this automated plasma cutter. This is because it gets the job done excellently.
Differences Between Laser and Plasma Cutting
When comparing laser and plasma cutting. The main discussions are the power source, the type of material that can be cut, speed, thickness, and cost.
Accuracy and Precision of Cutting
One of the major differences between laser cutting and plasma cutting is the accuracy of the cut. A laser beam is more focused than a plasma stream, so it can precisely locate objects in tight spaces. It can cut smooth, uniform curves with small tolerances and burr-free cutting surfaces. Plasma cutting, on the other hand, is less precise and has a larger kerf. With laser cutting, tolerances can be as low as ±0.030 mm. With plasma cutting, the tolerance can only be as low as ±0.1 mm.
Speed and Efficiency
The cutting speed of a plasma or laser cutter depends on the thickness of the material. The laser cutter is almost twice as fast as the plasma cutter when cutting plates less than 1.25 mm thick. However, plasma cutters are superior when cutting thicker plates.
In addition, cutting speeds vary depending on the power source and the material being cut. For example, a 200-watt laser can cut mild steel with a thickness of 3 millimeters at speeds of up to 10 meters per minute. On the other hand, laser cutters consume less energy than plasma cutters. This is another advantage of it.
Materials that Can Be Cut
The laser system can cut a wide range of materials. Such as steel, aluminum, copper, acrylic, thermoset plastics, rubber, and wood. In contrast, plasma cutting can only be used for conductive metals. This is because the plasma arc requires a circuit to move. The circuit is complete when the conductive material acts as a “ground”.
Although lasers can be used on many different materials. However, some of these materials present operational and environmental risks. For example, PVC can emit dangerous fumes. In addition, the type of laser you use can affect material compatibility.
Ready to get started on your next project? Get a personalized estimate for your parts machining needs.
Surface Finish
Laser-cut metal surfaces are smooth and burr-free, with sharp and clean edges. This is true even for narrow cuts and complex designs. As a result, there is no or very little post-processing required after cutting. On the other hand, plasma cutting produces slag and rougher edges. It therefore requires grinding, sandblasting, and other subsequent treatments.
In addition, the material type, thickness, and laser type affect the roughness value (Ra), which is typically 0.8 to 6 microns. In some cases, plasma cutting may provide a better surface finish than fiber laser cutting.
Costs and Operating Expenses
CNC plasma cutters have low setup costs, costing between $10,000 and $100,000. In contrast, a laser cutting machine is complex to set up, has advanced equipment, and is expensive. It typically costs between $50,000 and $500,000. As a result, laser-cutting machines also cost slightly more to run than plasma-cutting machines.
It is important to note that the cost of laser or plasma cutting depends on the complexity of the design, the accuracy required, and the degree of competition in the market. In China, the cost of laser cutting is 15-20 USD/hour, which is significantly lower than the cost in the U.S. and Europe. Yonglihao Machinery can provide you with high-quality laser cutting services at a lower cost.
Cutting Thickness
If you compare the thickness capability of laser cutting and plasma cutting. Then plasma cutting is very effective for thicker materials. On the other hand, laser cutting is limited to a thickness of 25 millimeters. Moreover, the thickness also depends on the material to be cut.
Applications
Plasma cutting is known for its speed and thickness in heavy industries such as shipbuilding and construction. Examples include structural beams, marine parts, agricultural machinery, and oil and gas components. Laser cutting is used in a wide range of applications where precision is required. Examples include jewelry, electronics, aerospace, and automotive.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser Cutting
The following are the most important advantages and disadvantages of laser cutting.
Advantages of Laser Cutting
- Automation and Precision: CNC lasers are able to process fine patterns with complex designs while maintaining very tight tolerances. This is possible because of digital control in the right direction via G and M codes.
- Clean and Burr-free Cutting: The laser cuts clean and sharp sides and edges.
- Material Versatility: It cuts metals, plastics, fabrics, composites, and many other materials.
- Speed and Efficiency: There is no need to readjust or adjust tools for design changes. In addition, laser cutting produces less material waste, uses less power, and is faster.
- No Hardening of the Workpiece: Non-shear cutting eliminates the risk of hardening the workpiece near the cut area.
Disadvantages of Laser Cutting
- Thickness Limitations: No matter how high the power of a laser cutter, it cannot cut plates thicker than 25 or 30 mm.
- Challenging for Reflective Metals: Materials that reflect light such as copper, brass, and silver are difficult to cut. This is because the beam of light only reaches part of their surface.
- High Costs: The set-up and running costs of the machine are higher than for other cutting methods. This means that for products that do not require a very smooth surface or high precision, this method may not be suitable.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Plasma Cutting
The following are the main advantages and disadvantages of plasma cutting.
Advantages of Plasma Cutting
- Cutting Thicker Materials: CNC-guided plasma torches are able to cut thicker materials faster and more efficiently, up to 150 millimeters thick for some materials.
- Cost Advantage: Plasma cutting is an inexpensive method for both light and heavy materials.
- Operational Safety: Instead of an oxygen-based cutting mechanism, it uses an inert gas to form a plasma jet inside the torch. It therefore offers maximum safety.
- Cutting Light-reflecting Metals: Unlike lasers, plasma cutting is excellent for light-reflecting metals such as silver.
Disadvantages of Plasma Cutting
- Conductive Metals Only: plasma cutting is only suitable for conductive metals and alloys.
- Risk of Thermal Damage: Plasma cutting creates a large heat-affected zone. This may damage the original thermal properties of the workpiece material.
- Poor Surface Quality: The plasma stream creates burrs and chips, resulting in a rougher cut of the metal.

How to Choose the Right Cutting Method for Your Project
Choosing a plasma or laser cutter for your project depends on many factors. For example, the difficulty of the design and your budget. In addition, the material you are working with and your final requirements will also influence the choice.
Here are four important things to consider when choosing the right method:
Material Type
What shape of workpiece or plate are you cutting? Is it electrically conductive? If it is a non-conductive material, then you can only choose a laser cutter. Also, even if you are sure about using a laser cutter, check the compatibility of your material with the available laser types (CO2, fiber, and crystal).
Thickness and Dimensions
If your design has any thicker parts that are more than 30 mm thick, choose plasma cutting. Otherwise, check the cutting speeds of both technologies for the specified thickness. On the other hand, smaller parts are well suited for laser cutting. This is because laser cutting produces a smaller heat-affected area.
Accuracy and Cost Objectives
The smaller the tolerances, the higher the costs tend to be. Therefore, try to obtain the best possible accuracy at the lowest possible cost. Then check which method fits your budget better without losing the required precision and accuracy.
Complexity of Design
Complex and precise cuts can only be achieved with a CNC laser cutting machine. For designs containing micro-contours, sharp corners, small radii (<1mm), engraving, etc., a CNC laser cutter is the right choice.
Summary
Aside from the many ways in which laser cutting and plasma cutting differ, both types of cutting are valuable in metalworking projects. In addition, the choice of cutting type depends on the specific requirements of the project. This includes the type of material, the accuracy required, and the budget. You can check the cost and expected results of each method.
If you are still unsure which one to choose, consult a professional in the field. At Yonglihao Machinery, we can provide you with professional CNC laser cutting services. In addition, our engineers will provide consultation on design optimization, cost analysis, and the comparative advantages of each method before entering the production phase.
FAQ
Which Cutting Method Costs Less?
Plasma cutting is less expensive than laser cutting. This is because the equipment required for plasma fabrication and cutting is simpler. However, if functionality or performance is important, laser cutting is accurate enough to justify the price.
Can These Two Methods Cut the Same Thing?
They can both cut conductive metals but with different ranges and qualities. Laser cutters can cut mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and some non-metallic materials. Plasma, on the other hand, can cut steel, stainless steel, and other metallic materials.
What Is the Maximum Cutting Thickness for Laser Cutting vs Plasma Cutting?
The maximum cutting thickness of a laser cutter is 30 mm (about 1 inch). Plasma cutters have a maximum cutting thickness of 50 mm (about 2 inches). In addition, some high-powered plasma tools can cut up to 100 millimeters or more.

